Blackerries, raw
Scientific Name: Rubus spp.
NDB No: 09042
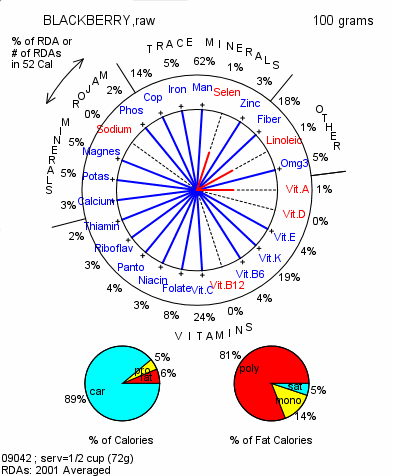 BLACKBERRIES are unusually rich in antioxidant polyphenols, tannins, and other protective substances. They ripen in summer, but frozen berries are always available. Try them in fruit salads, on cereal and pancakes, and in smoothies.
BLACKBERRIES are unusually rich in antioxidant polyphenols, tannins, and other protective substances. They ripen in summer, but frozen berries are always available. Try them in fruit salads, on cereal and pancakes, and in smoothies. Their small fat content is notably polyunsaturated and of the omega-3 type. They contain about 5% protein and thus amino acids, but in unreported amounts (question marks). Relative to their few calories, blackberries contain adequate amounts of most nutrients shown. Jam is a poor source; a tablespoon might contain one berry but more calories than 1/2 cup of berries. Their small fat content is notably polyunsaturated and of the omega-3 type. They contain about 5% protein and thus amino acids, but in unreported amounts (question marks). Relative to their few calories, blackberries contain adequate amounts of most nutrients shown. Jam is a poor source; a tablespoon might contain one berry but more calories than 1/2 cup of berries.
The blackberry is actually an ancient fruit, prescribed by the Ancient Greeks for gout, mentioned in the Bible, and commonly written about in British folklore.
Wild blackberries are relatives of the rose and the soft, juicy fruit grows on thorny bushes or trailing vines. Just like a raspberry, the blackberry is called an "aggregate fruit" because each berry is really a cluster of tiny fruits, or druplets. Each druplet has a seed, and, unlike raspberries, blackberry druplets remain centered around the core even after the berry is picked.
Blackberries abound in antioxidants, such as anthocyanin pigments, responsible for the purplish-black color of blackberries and may impart health benefits because of their antioxidant properties. Additional antioxidants in blackberries are vitamins C and E, and ellagic acid; all may provide protection against cancer and chronic disease. Cooking does not seem to destroy ellagic acid, so even blackberry jams and desserts retain ellagic acid health benefits. Interestingly, blackberries are a natural source of salicylate, an active substance found in aspirin. Potential benefits have yet to be explored and some experts advise caution to particularly aspirin-sensitive individuals. Because of their many tiny seeds, blackberries are a source of soluble fiber, such as pectin.
| Proximates
|
|
Water
|
g
|
63.47
|
|
Energy
|
kcal
|
31
|
|
Energy
|
kj
|
130
|
|
Protein
|
g
|
1.00
|
|
Total lipid (fat)
|
g
|
0.35
|
|
Ash
|
g
|
0.27
|
|
Carbohydrate, by difference
|
g
|
6.92
|
|
Fiber, total dietary
|
g
|
3.8
|
|
Sugars, total
|
g
|
3.51
|
|
Sucrose
|
g
|
0.05
|
|
Glucose (dextrose)
|
g
|
1.66
|
|
Fructose
|
g
|
1.73
|
|
Lactose
|
g
|
0.00
|
|
Maltose
|
g
|
0.05
|
|
Galactose
|
g
|
0.02
|
|
Starch
|
g
|
0.00
| | Minerals
|
|
Calcium, Ca
|
mg
|
21
|
|
Iron, Fe
|
mg
|
0.45
|
|
Magnesium, Mg
|
mg
|
14
|
|
Phosphorus, P
|
mg
|
16
|
|
Potassium, K
|
mg
|
117
|
|
Sodium, Na
|
mg
|
1
|
|
Zinc, Zn
|
mg
|
0.38
|
|
Copper, Cu
|
mg
|
0.119
|
|
Manganese, Mn
|
mg
|
0.465
|
|
Selenium, Se
|
mcg
|
0.3
| | Vitamins
|
|
Vitamin C, total ascorbic acid
|
mg
|
15.1
|
|
Thiamin
|
mg
|
0.014
|
|
Riboflavin
|
mg
|
0.019
|
|
Niacin
|
mg
|
0.465
|
|
Pantothenic acid
|
mg
|
0.199
|
|
Vitamin B-6
|
mg
|
0.022
|
|
Folate, total
|
mcg
|
18
|
|
Folic acid
|
mcg
|
0
|
|
Folate, food
|
mcg
|
18
|
|
Folate, DFE
|
mcg_DFE
|
18
|
|
Vitamin B-12
|
mcg
|
0.00
|
|
Vitamin A, IU
|
IU
|
154
|
|
Vitamin A, RAE
|
mcg_RAE
|
8
|
|
Retinol
|
mcg
|
0
|
|
Vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol)
|
mg
|
0.84
|
|
Tocopherol, beta
|
mg
|
0.03
|
|
Tocopherol, gamma
|
mg
|
0.96
|
|
Tocopherol, delta
|
mg
|
0.65
|
|
Vitamin K (phylloquinone)
|
mcg
|
14.3
| | Lipids
|
|
Fatty acids, total saturated
|
g
|
0.010
|
|
4:0
|
g
|
0.000
|
|
6:0
|
g
|
0.000
|
|
8:0
|
g
|
0.000
|
|
10:0
|
g
|
0.000
|
|
12:0
|
g
|
0.000
|
|
14:0
|
g
|
0.000
|
|
16:0
|
g
|
0.009
|
|
18:0
|
g
|
0.002
|
|
Fatty acids, total monounsaturated
|
g
|
0.034
|
|
16:1 undifferentiated
|
g
|
0.000
|
|
18:1 undifferentiated
|
g
|
0.032
|
|
20:1
|
g
|
0.003
|
|
22:1 undifferentiated
|
g
|
0.000
|
|
Fatty acids, total polyunsaturated
|
g
|
0.202
|
|
18:2 undifferentiated
|
g
|
0.134
|
|
18:3 undifferentiated
|
g
|
0.068
|
|
18:4
|
g
|
0.000
|
|
20:4 undifferentiated
|
g
|
0.000
|
|
20:5 n-3
|
g
|
0.000
|
|
22:5 n-3
|
g
|
0.000
|
|
22:6 n-3
|
g
|
0.000
|
|
Cholesterol
|
mg
|
0
| | Other
|
|
Alcohol, ethyl
|
g
|
0.0
|
|
Caffeine
|
mg
|
0
|
|
Theobromine
|
mg
|
0
|
|
Carotene, beta
|
mcg
|
92
|
|
Carotene, alpha
|
mcg
|
0
|
|
Cryptoxanthin, beta
|
mcg
|
0
|
|
Lycopene
|
mcg
|
0
|
|
Lutein + zeaxanthin
|
mcg
|
85
|
USDA National Nutrient Database for Standard Reference, Release 17 (2004)
|